.PNG)
Cell Types and Cell Structure Presentation Biology
Cilia and flagella are fine, whiplike/hairlike structures that extend from the body of a variety of cells. While they vary in terms of length and numbers in different types of cells (as well as patterns of movement), cilia and flagella are generally identical in structure and composition.
/ciliated_epithelial_cells-5a7cb8926edd650036eb92da.jpg)
Cilia and Flagella Function
Structure of a cell > Tour of a eukaryotic cell The cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton. Microtubules, microfilaments (actin filaments), and intermediate filaments. Centrioles, centrosomes, flagella and cilia. Introduction What would happen if someone snuck in during the night and stole your skeleton?
Difference Between Cilia And Flagella In Eukaryotes cloudshareinfo
The bending of cilia (and flagella) has many parallels to the contraction of skeletal muscle fibers. Testing the Model. Remember, the partial microtubules do not extend as far into the tip as the complete microtubules. So if a slice is made a short distance back from the tip: A straight cilium should show the complete pattern (center of diagram).
Biology diagram present different of cilia and flagella in eukaryote and prokaryote organism
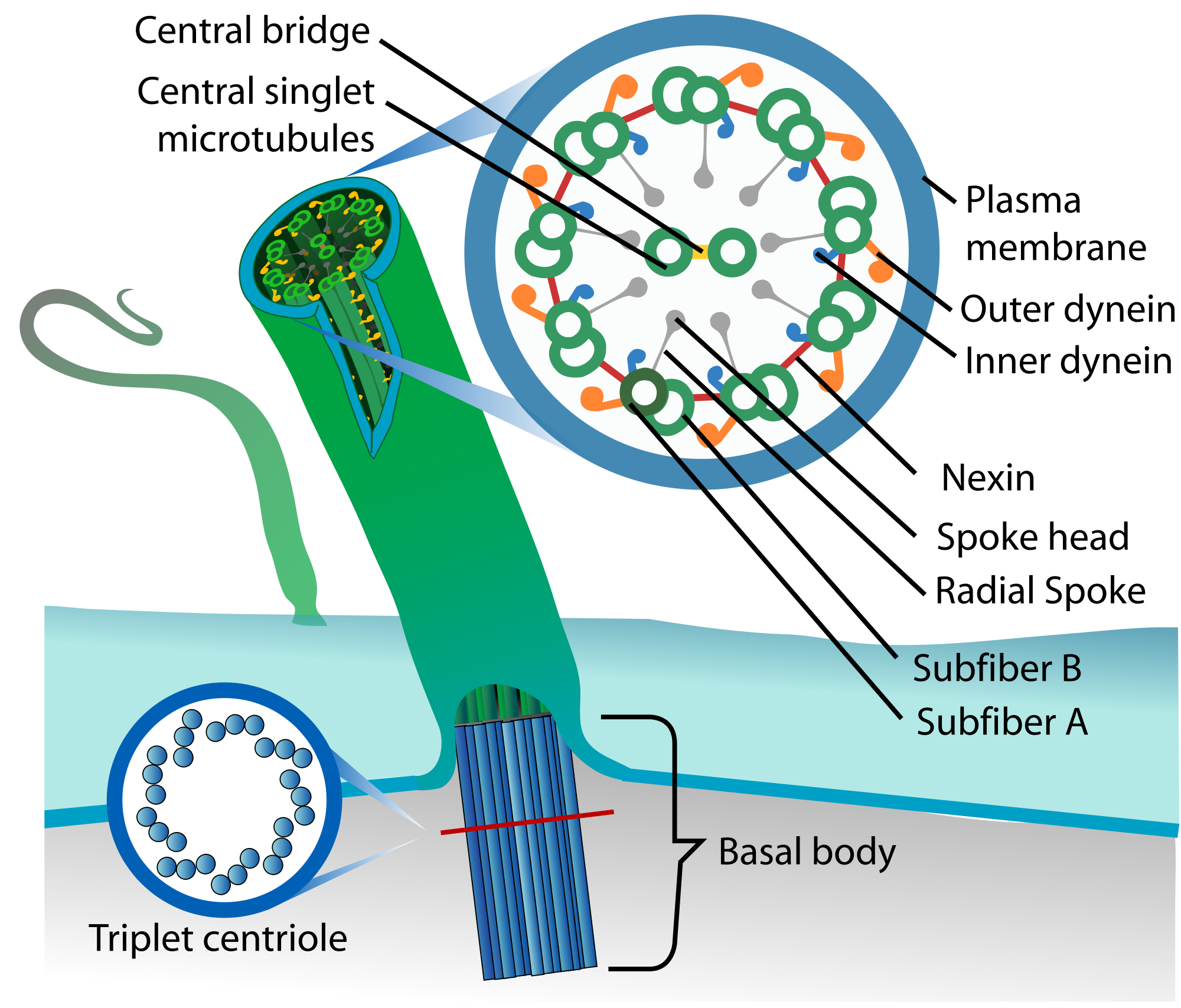
Cilia and flagella are conserved, motile, and sensory cell organelles involved in signal transduction and human disease. Their scaffold consists of a 9-fold array of remarkably stable doublet microtubules (DMTs), along which motor proteins transmit force for ciliary motility and intraflagellar transport.

Top 115+ Cilia and flagella plant or animal cell
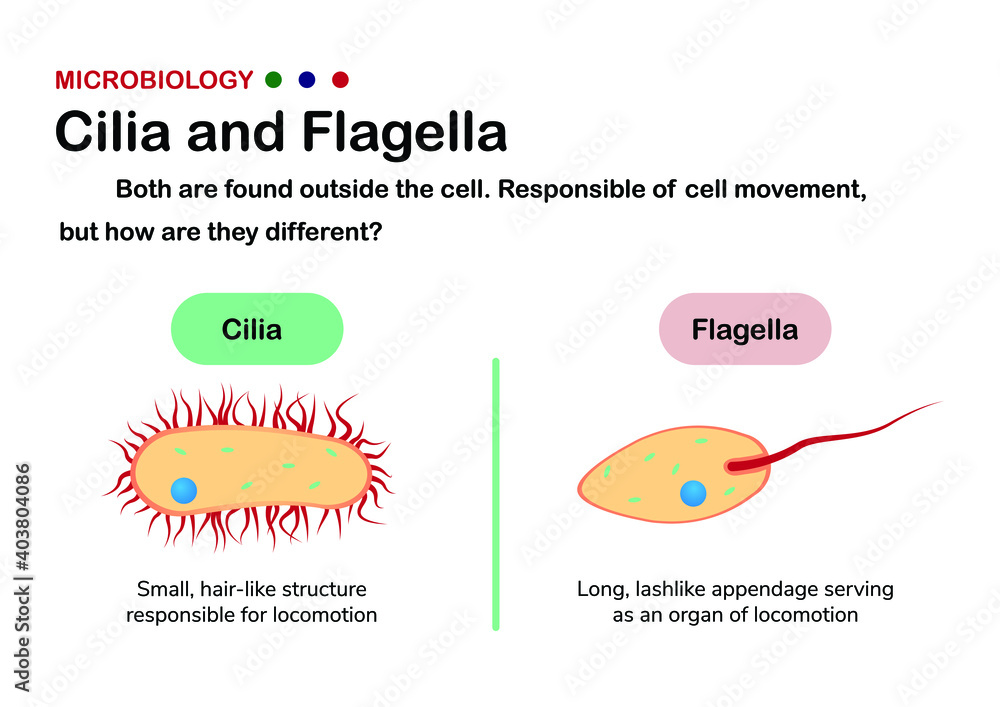
Flagella (singular = flagellum) are long, hair-like structures that extend from the plasma membrane and are used to move an entire cell, (for example, sperm, Euglena ). When present, the cell has just one flagellum or a few flagella. When cilia (singular = cilium) are present, however, they are many in number and extend along the entire surface.
Animal Cell Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram
Cilia and Flagella are cytoplasmic filamentous structures which protrude through the cell wall. They are the cell's minute, highly distinct appendages. An entire cell is propelled by its flagella (singular form: flagellum), which are long, hair-like projections that protrude from the plasma membrane.
Flagella Definition Structure Types Arrangement Functions Examples Riset
A flagellum or flagella is a lash or hair-like structure present on the cell body that is important for different physiological functions of the cell. The term 'flagellum' is the Latin term for whip indicating the long slender structure of the flagellum that resembles a whip.

Flagellum & Cilia Wikimedia Commons CCA 3.0 Unported by Urutsegh and Kohidai Cell Structure
So this right over here is a picture of the amoeba Chaos carolinense. And what you see here is a projection coming off from the main part of the cell, and this is called a pseudopod, which is referring to it being a false foot. The pod is coming from the same root word as podiatry, which is referring to the foot.

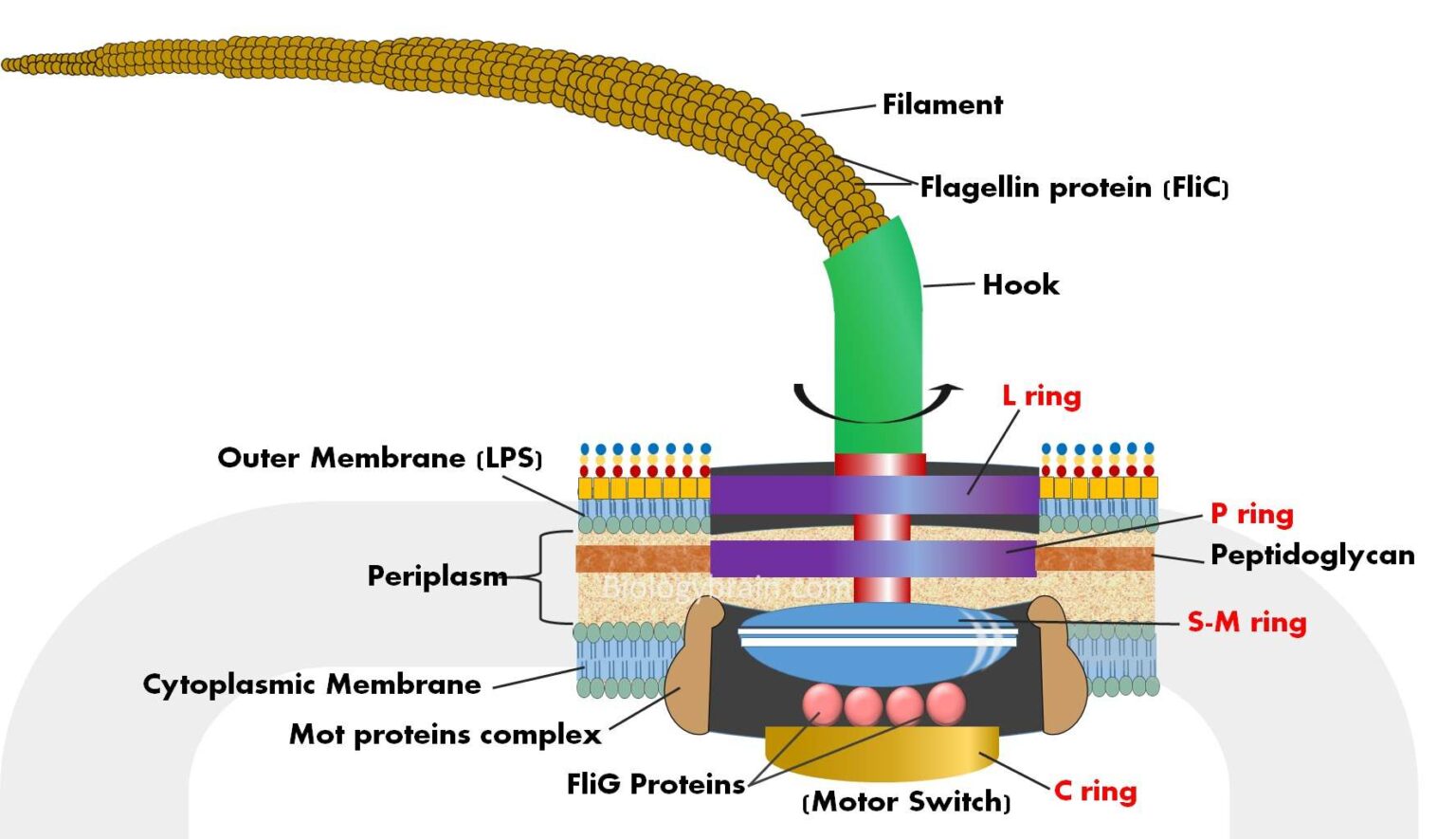
2 rings in the basal body Google Search Plasma membrane, Microbiology, Cell wall
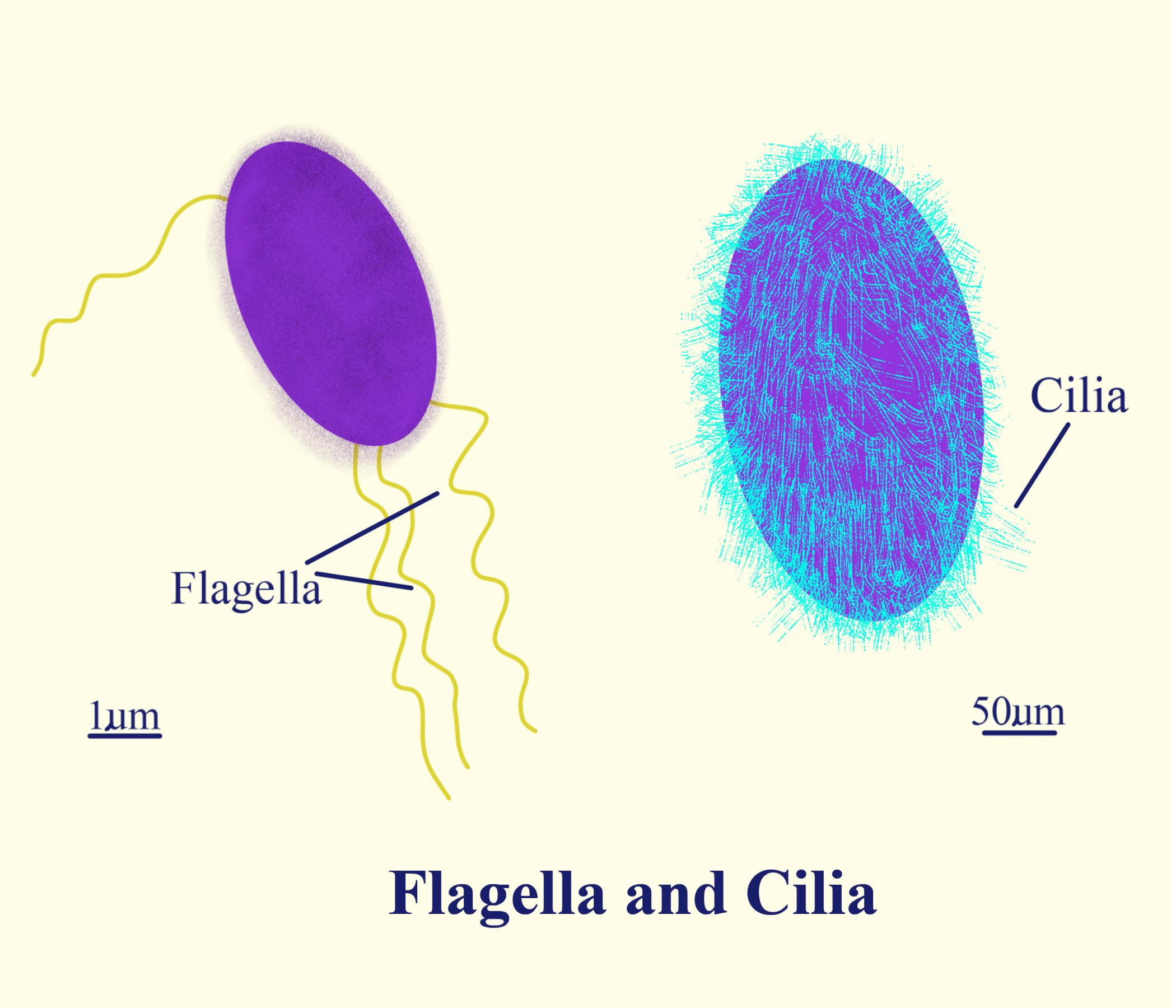
Cilia and flagella are cell organelles that are structurally similar but are differentiated based on their function and/or length. Cilia are short and there are usually many (hundreds) cilia per cell. On the other hand, flagella are longer and there are fewer flagella per cell (usually one to eight).

Blink Activity BlinkLearning
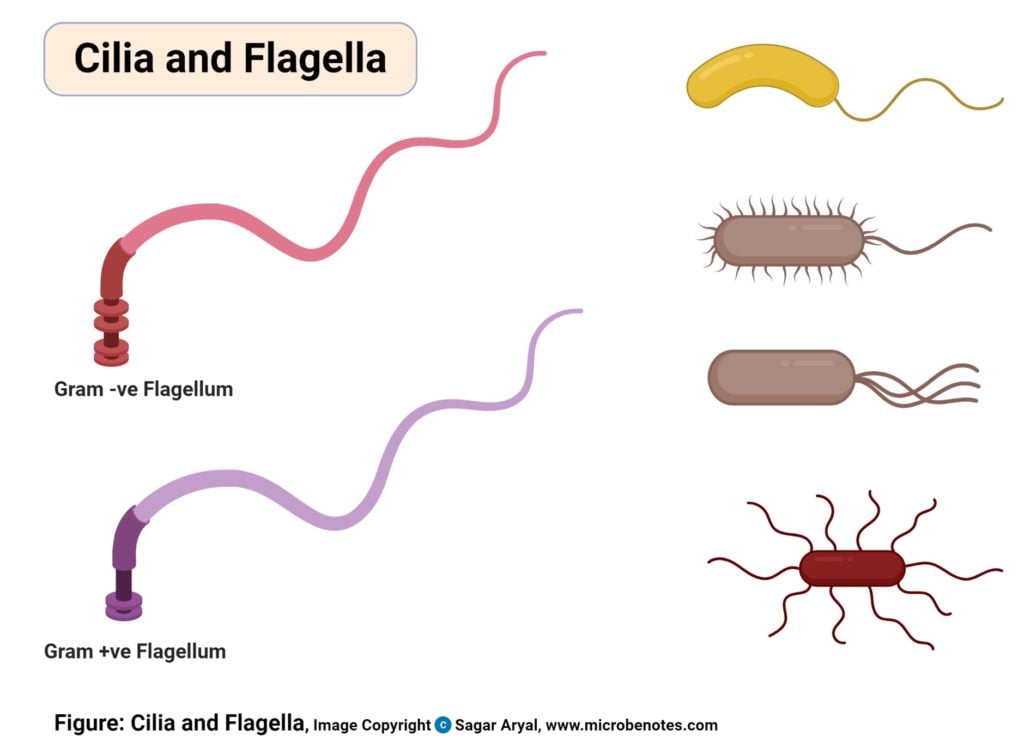
Cilia and Flagella Frequently Asked Questions on Flagella Bacterial Flagella Structure The flagella is a helical structure composed of flagellin protein. The flagella structure is divided into three parts: Basal body Hook Filament Basal Body It is attached to the cell membrane and cytoplasmic membrane.
Which Of The Following Is Not A Function Cilia And Flagella About Flag Collections
Figure 7.7.7 7.7. 7 .7.3: A cilium (plural cilia) is an organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Cilia are slender protuberances typically extending some 5-10 micrometers outwards from the cell body. There are two types of cilia: motile cilia, which constantly beat directionally, and non-motile—or primary—cilia, which typically serve as.
PPT Cilia and Flagella in Cell Structure PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID333456
Nature Education 3 (9) :54 What is a primary cilium? Learn how an organelle can be both a sensing organ and a transport machine. Aa Aa Aa Eukaryotic flagella and cilia have long been recognized.
7.7 Flagella and Cilia Biology LibreTexts
Cilia and flagella are formed from specialized groupings of microtubules called basal bodies. If the protrusions are short and numerous they are termed cilia. If they are longer and less numerous (usually only one or two) they are termed flagella. What Are Their Distinguishing Characteristics?

Schematic drawing of eukaryotic flagella ultrastructure (A)... Download Scientific Diagram
Cilia (L. cilium =eye lash) and flagella (Gr. flagellum - whip) are fine hair-like protoplasmic outgrowths of cells and take part in cell motility. These organelles were first reported by Englemann (1868). Cilia and flagella are basically similar but they vary in number, length and patterns of movement.

Radial spoke of axoneme of cilium Semantic Scholar
Structure of Flagella and Cilia: They are fine hair like movable protoplasmic processes of the cells which are capable of producing a current in the fluid medium for locomotion and passage of substances. Flagella are longer (100-200 µm) but fewer. Only 1-4 flagella occur per cell, e.g., many protists, motile algae, spermatozoa of animals.

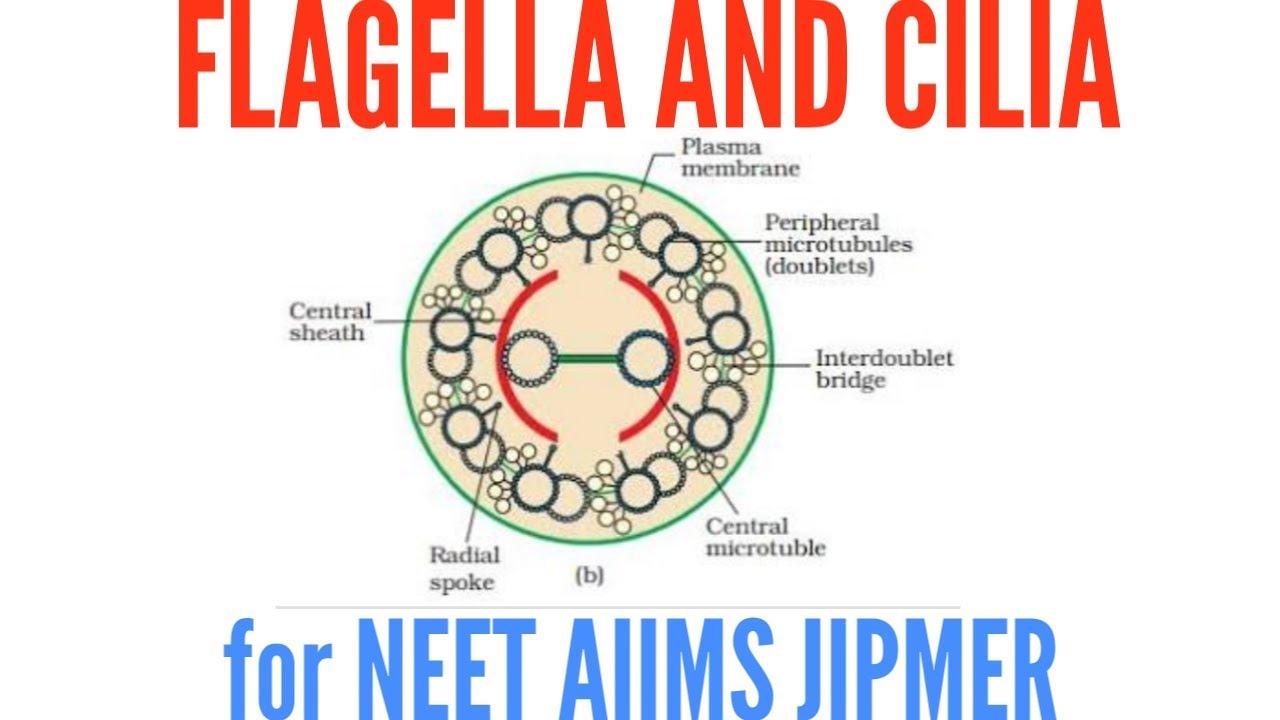
draw cilia/flagella 9+2 arrangement Brainly.in
Cilia and flagella have the same internal structure. The major difference is in their length. Cilia and flagella move because of the interactions of a set of microtubules inside. Collectively, these are called an "axoneme", This figure shows a microtubule (top panel) in surface view and in cross section (lower left hand panel)..